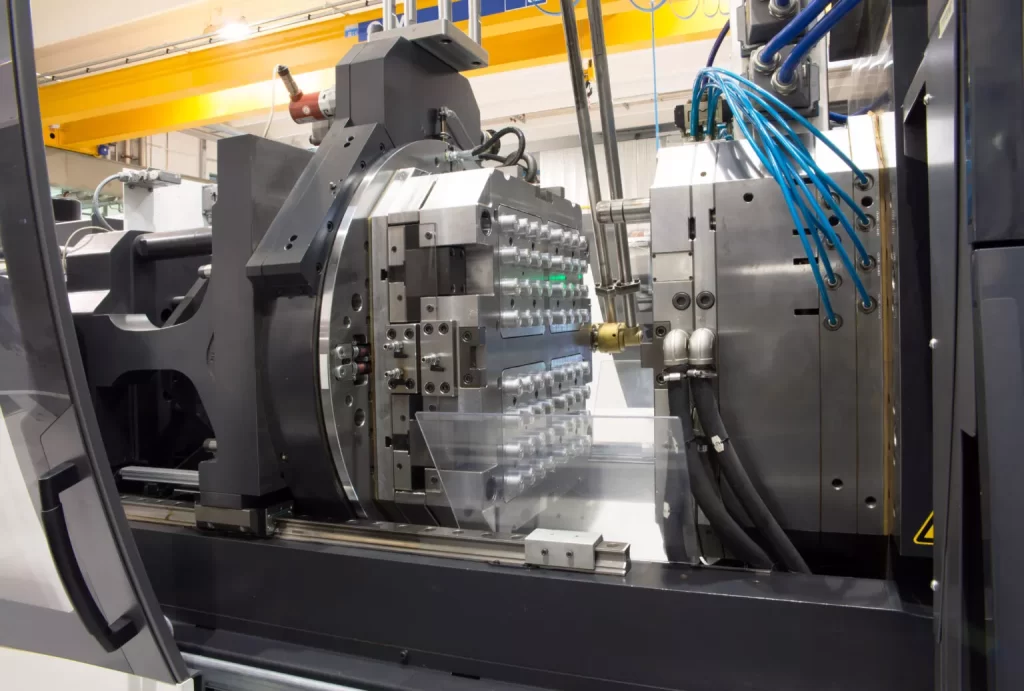
Plastic is probably one of the most versatile materials on the planet. With its appearance common in numerous industries ranging from automotive to medical supplies, plastic can take any size, shape, and form.
While it is plastic’s own properties that often get the credit for the material’s versatility, the process involved in manufacturing the plastic parts is also to be credited for making plastic products’ applicability and usage so widespread, economical, and diverse.
This process is plastic injection molding and is often the most preferred method for producing plastic parts that we use every day.
The plastic injection molding market size is expected to grow at a CAGR of almost 5% and reach over $400 billion by 2030 due to its versatility and other benefits.
What is plastic injection molding, how is it done, and what types of plastics can you mold successfully through this process? We answer these questions and more in this blog. Stay tuned!
Understanding Plastic Injection Molding: The Basics
Plastic injection molding is a complex process that is capable of manufacturing an unimaginable variety of plastic parts. It uses thermoplastic and melts it before molding it into the required shape and size.
Of course, this is an oversimplification of all the nuances involved in the process. In reality, the plastic injection molding machine carries out complex processes using tightly controlled variables to produce the right parts.
The plastic injection molding process promises high production volume and can deliver plastic parts in bulk with no comprises on quality, as long as the process variables are tightly controlled.
Besides allowing for high production volume and ensuring consistent quality, the process is also as flexible as you can imagine. You can manufacture any type of plastic part, whether it is simple or complicated without any changes to the process. All you have to do is change the mold, adjust the variables, and get going.
However, you have to get a new mold made before creating any new product. And molds are expensive. But that’s the only cost-intensive part of the process as once the mold is ready and fitted into the machine, the parts can be manufactured in huge quantities at minimal cost. This is another one of plastic injection molding’s benefits.
Understanding Plastic Injection Molding: The Process
We have only scratched the surface of the plastic injection molding process so far. There is a lot that goes behind the seemingly simple plastic products we use every day.
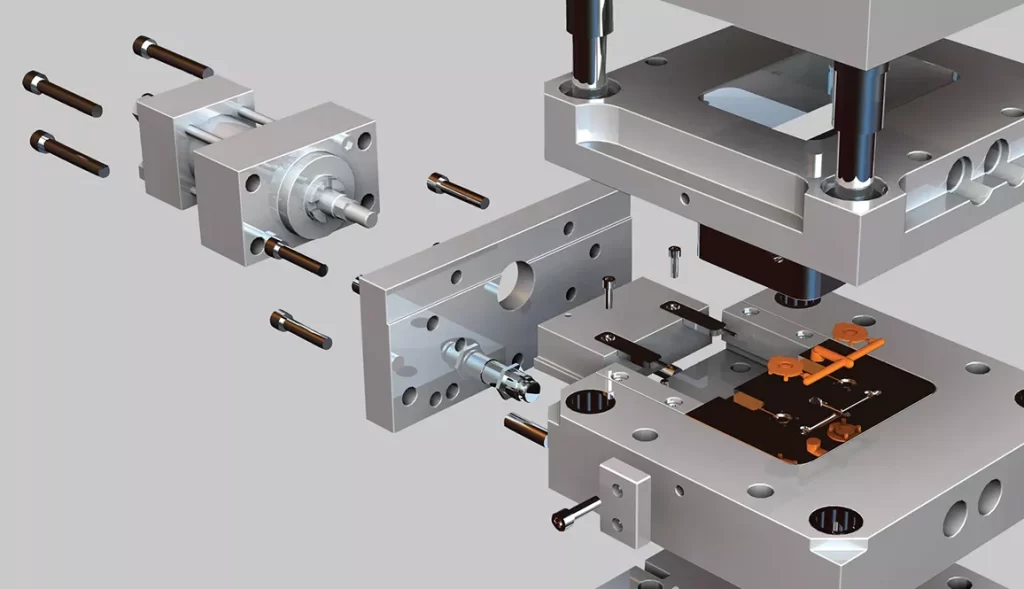
The plastic injection molding process can be broadly divided into four stages. But before we discuss those stages, let’s take a minute to understand the plastic injection molding machine. This will help us get a grip on the process better.
The Injection Molding Machine:
The injection molding machine consists of many parts. The most important of these parts include:
Hopper
The hopper is essentially a feeder present at the top of the injection molding machine. It serves to feed plastic granules into the barrel.
Barrel
Barrel is where the melting takes place. The plastic granules come into the barrel through the hopper where it is melted so it can be injected into the mold.
Heater
The heater is present around the barrel and runs along its length. It heats the plastic granules and melts them to ensure the material is ready to be injected.
Reciprocating Screw
The reciprocating screw is a crucial component. It rotates within the barrel and moves back and forth through the molten plastic to inject it into the mold.
Nozzle
The nozzle appears at the end of the barrel and screw system and serves to direct the flow of molten plastic from the barrel into the mold cavity.
Mold
The mold consists of two parts, the mold cavity and core. The cavity is where the molten plastic flows into and is responsible for producing the external surface of the part. The core closes into the cavity and creates the internal surface of the final plastic part.
Both the molds are mounted on platens, one of them is movable while the other is fixed.
Gate
The gate is a vital component of the injection molding process that is a part of the runner system. The runner system channels the molten plastic through the mold and into the cavity. A gate exists at the point where the molten plastic exits the runner system and goes into the mold cavity.
The Plastic Injection Molding Process
The plastic resins have to go through a multi-stage process before they can come out in the shape of a nicely designed part. These stages include:
Stage 1: Clamping
Clamping is when the two parts of the mold are securely closed together. This is an important stage that requires the right pressure called the clamping pressure to be maintained to prevent leakages and defects like flashing from appearing on the formed part.
Stage 2: Injection
The plastic granules are fed into the barrel where they are heated to form molten plastic.
Once the molds are tightly closed, this molten plastic is fed into the molds from the heated barrel using the screw. The screw rotates inside the barrel and pushes the molten plastic through the nozzle into the runner system which then feeds it into the mold through gates present at the end of the runners. This step is called injection.
Stage 3: Cooling
Once the plastic is fully fed into the mold, the cooling process begins. The coolant runs through the pipes along the mold carrying the molten plastic to solidify the part. Cooling a newly formed plastic part can take anywhere from milliseconds to minutes depending upon the complexity of the part.
Stage 4: Ejection
Once the part is fully cooled and completely solidified, the screw rolls back into the barrel, the molds open and the ejection system comes into play.
Ejector pins or ejector plates push the solidified part out of the mold. The design and placement of these pins are both highly precise and well thought-out to ensure the ejection process does not lead to any part defects.
Once the part is out of the machine, the molds close, and the screw comes back into action to move on to the next part.
There are many variables involved throughout each stage of the plastic molding process. These include injection pressure, clamping pressure, and temperature to name a few. All of these variables must be tightly controlled through all the stages of the injection molding process to ensure consistency in part quality and minimize defects.
What Types of Plastics Can You Use in Plastic Injection Molding?
We know plastic injection molding is a versatile process. One of these factors is its ability to take in a wide variety of plastics, melt them, and mold them into whatever shape or size is needed.
Below is a list of some of the most common types of plastics you can use in the injection molding process:
PVC (Polyvinyl Chloride)
PVC is a soft and malleable plastic that is often used in the manufacturing of food packaging, drinking water bottles, toys, water pipes, etc. It is very versatile and known for its durability and chemical resistance.
PP (Polypropylene)
Polypropylene is another thermoplastic that shows strong resistance to chemicals while also giving a hygienic finish. Its ability to keep edible and sterile materials free from contamination makes the thermoplastic a go-to choice in medical industries. Besides that, PP is also used to create common household items like dishes and containers.
PET (Polyethylene Terephthalate)
PET is also lightweight and strong, which is why it can be injection molded to make beverage bottles, food containers, etc.
Polymethyl Methacrylate (PMMA)
PMMA, popularly known as Acrylic, can also be molded into any shape or form using the injection molding process. The plastic has a transparent finish and high impact resistance which is why it is often used to make screens used in retail, rigid packaging, glasses, and other optical devices.
Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene (ABS)
ABS is a tough, impact-resistant thermoplastic widely used in injection molding for making transparent yet strong protective packaging for cosmetic and beauty industry products.
Each of these plastics has its own, unique characteristics and properties which make them suitable for various end products. The thermoplastics are carefully selected as per the design requirements to ensure good quality of the end product.
Conclusion
Plastic injection molding is a versatile process that can help manufacture a wide variety of products in bulk. Its capability to take high production volume and create hundreds of parts while maintaining design consistency is what makes it preferable for plastic part manufacturing.
Plastic is fed into the machine in the form of granules or pellets. It is then melted within the barrel and fed into the molds before being solidified and ejected. This happens through four stages as we have discussed above.
Many different plastics may be used in the injection molding process. All you need to do is adjust process variables, fix the required mold, and start molding with the plastic you want.
Post-processing may also be needed in certain cases if the part comes out with defects like flashing or require decoration.